-
 2026-02-11
2026-02-11Pulsar’s Oryx LRF XG35 Bridges Compact and Prem...
Pulsar's thermal monocular lineup spans a wide range—from the ultra-compact Axion XQ19 at just over a thousand dollars to the modular Telos platform pushing past five grand. But there's a... -
 2026-01-22
2026-01-22Pulsar Trail 3: Back to Basics
The Pulsar Trail line has long been associated with durability, field-ready ergonomics, and dependable thermal performance. With the Trail 3 series, Pulsar returns to the design principles that defined the... -
 2026-01-20
2026-01-20Thermal Scope Performance in Real-World Conditions
A thermal scope allows users to detect heat rather than rely on reflected or amplified light. That fundamental difference reshapes how optics perform at night, in poor weather, and across... -
 2026-01-13
2026-01-13Thermal Scope Discipline on Grazing Land
A few days ago, I learned a new phrase to hunt by: if it has a neck, it ain't a pig. Simple. Memorable. And once you're staring through a thermal... -
 2026-01-09
2026-01-09Thermal Scopes for Coyote Hunting: Complete Equ...
Thermal scopes for coyote hunting have revolutionized predator control, giving hunters a decisive advantage during nighttime operations. When combined with the right weapons and equipment, thermal technology transforms challenging coyote... -
 2025-12-29
2025-12-29Is a Thermal Monocular Worth It?
Every hunter eventually asks the same question when they first look at thermal optics: Is this actually worth the money, or is it just another gadget? The honest answer depends... -
 2025-12-09
2025-12-09Pulsar Announces December-Only Pricing on Selec...
Pulsar is rolling out month-long December pricing across several of its leading thermal optics, including key models in the Axion, Oryx, Talion, and Thermion families. These reductions run from December... -
 2025-12-02
2025-12-02How to Choose the Right Thermal Binoculars
Thermal binoculars unlock the unseen world. Whether you’re glassing ridgelines for game, conducting nighttime surveillance, or tracking movement in low light, the right pair turns darkness into clarity. But not... -
 2025-11-17
2025-11-17What Is Thermal Imaging Used For?
Thermal imaging turns heat into vision. Every object on Earth emits infrared radiation—energy invisible to the naked eye but detectable by modern sensors. A thermal imager captures those minute differences... -
 2025-10-28
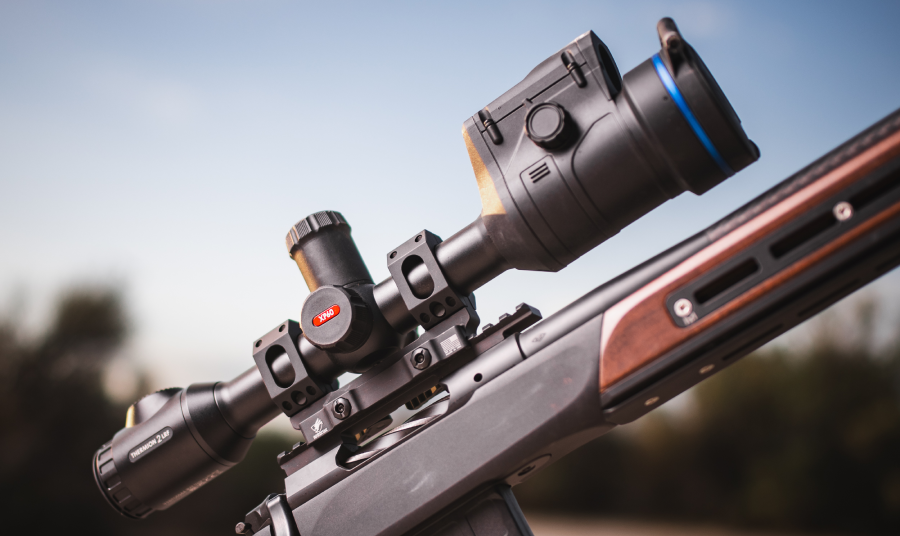
2025-10-28How to Choose Your First Thermal Sight
You’re about to spend several thousand dollars on a piece of gear that claims to see heat, track animals through fog, and make you the apex predator of the night.... -
 2025-10-10
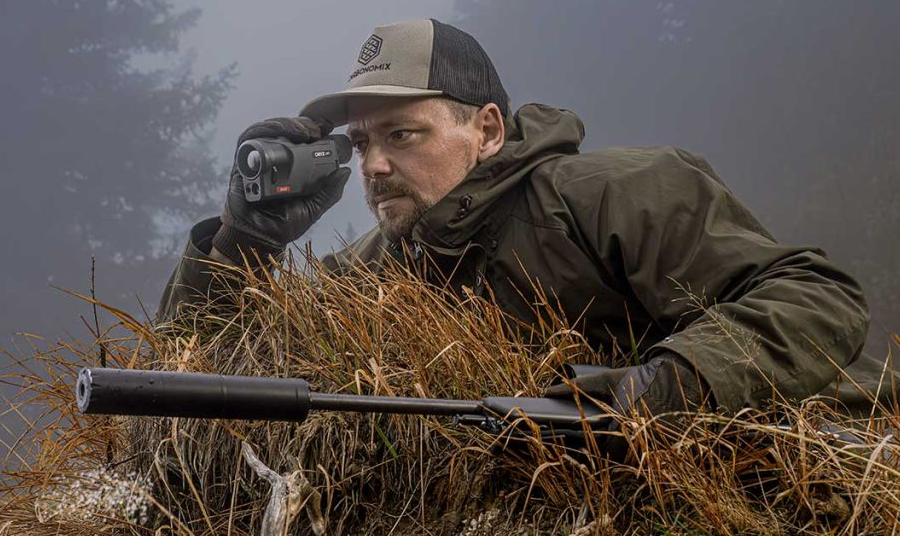
2025-10-10Thermal Night Vision: Pairing Monoculars with R...
A thermal riflescope is built for shooting, not for searching. Walking through the woods at night with your rifle shouldered, peering down the scope at every sound, is as impractical... -
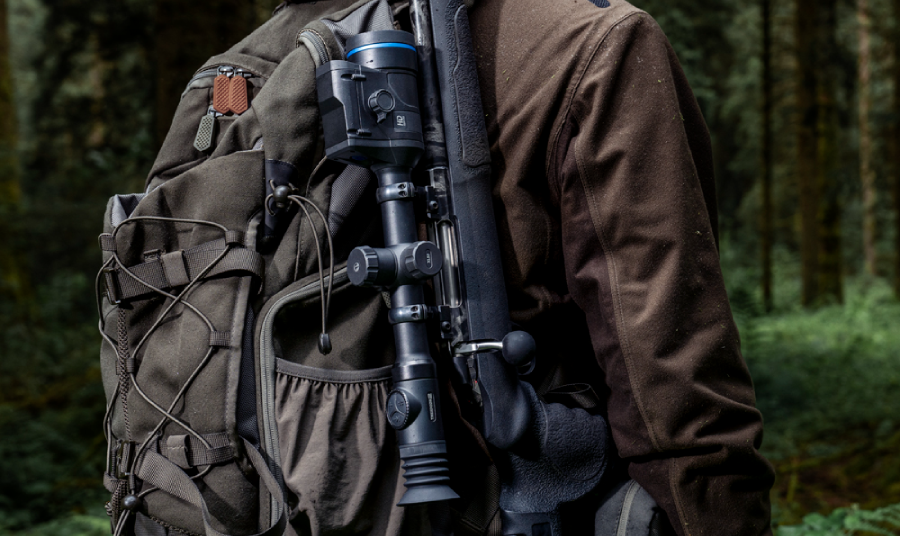 2025-09-25
2025-09-25What is a Thermal Sight?
A thermal sight, sometimes called a thermal scope, is a type of riflescope that doesn’t rely on visible light at all. Instead, it shows you heat. Every animal, person, or... -
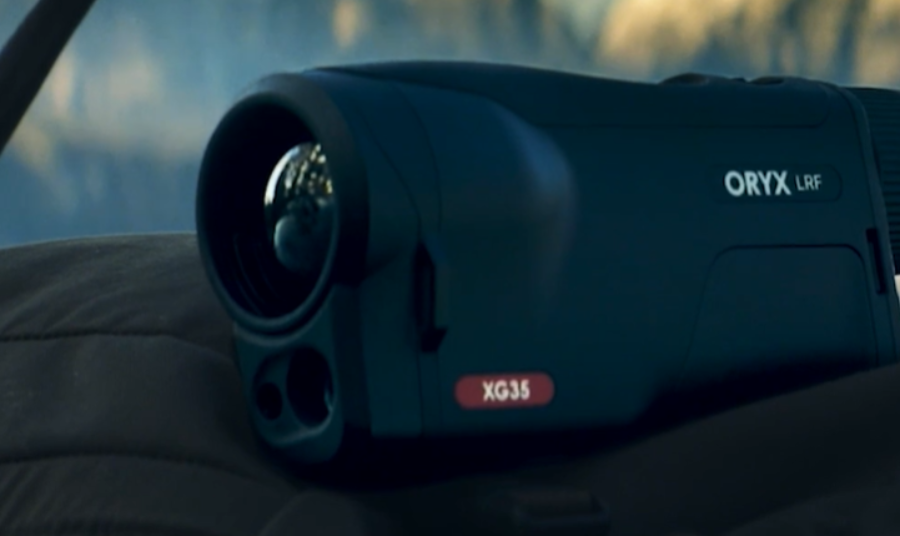 2025-09-03
2025-09-03Do You Really Need a 1,640-Yard Rangefinder for...
Most hunting shots never stretch past 100 yards. A whitetail in the timber or a hog rooting under a feeder is usually inside bow range, not across a canyon. So... -
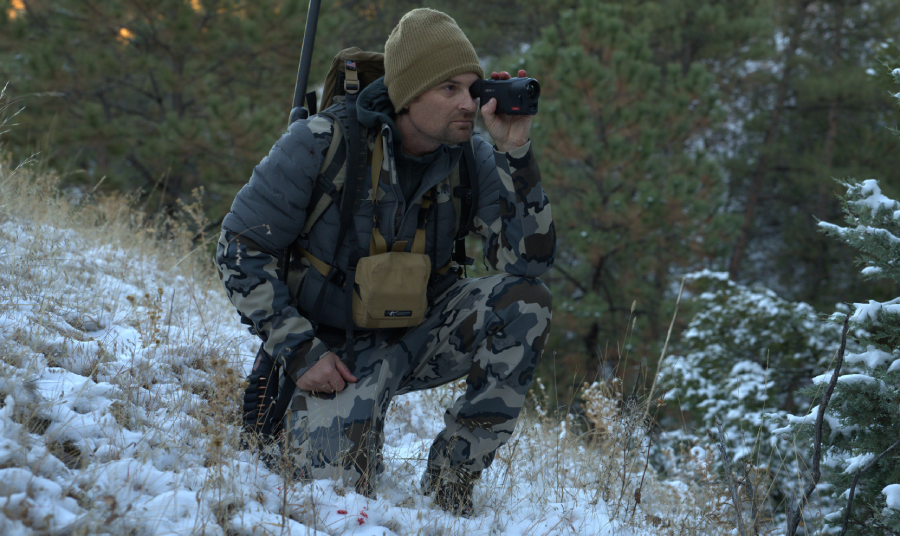 2025-08-21
2025-08-21Practical Hunting Tips with the Pulsar Oryx LRF...
Thermal optics have become a go-to tool for hunters who want to track game more efficiently after dark. Animals like hogs, coyotes, and raccoons are most active when visibility is... -
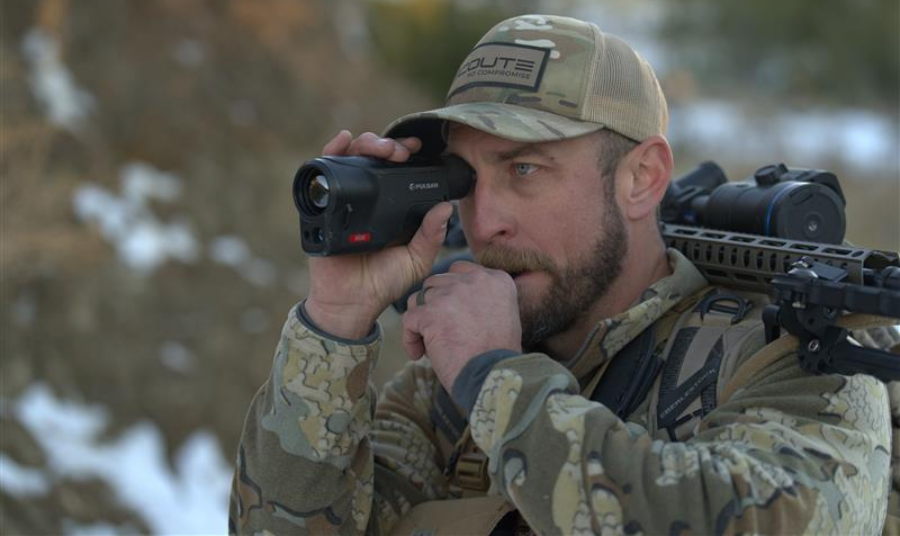 2025-08-15
2025-08-15Why the Pulsar Oryx LRF Earns Its Place in a Hu...
When Pulsar released the Oryx LRF thermal monocular, it entered a market already crowded with capable optics. Yet early adopters are reporting that this unit brings together a rare combination...
Item added to your cart